1. Diagram of the Danish higher education system
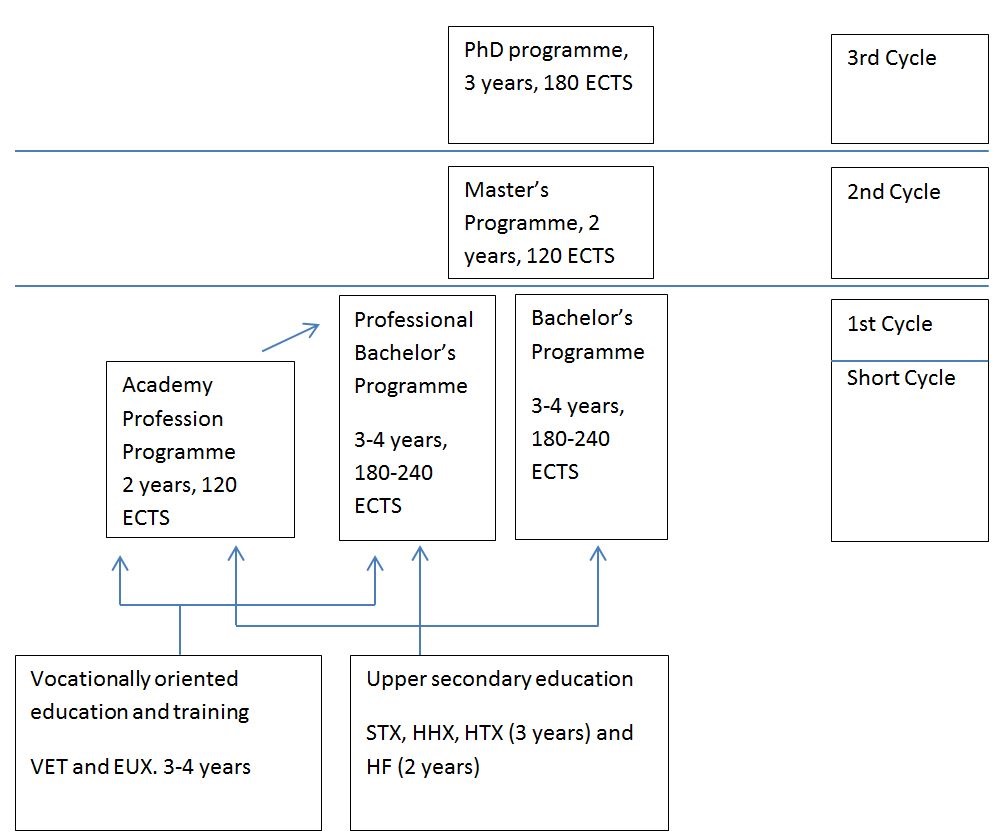
2. Types of higher educational institutions
| National name | English name | Quality assurance | NQF / EQF | Types of qualifications offered |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Erhvervsakademi | Business academy | The Danish Accreditation Institution | 5-6/5-6 | Academy Profession (AP) degree, Professional Bachelor’s degree. |
| Professionshøjskole | University colleges | The Danish Accreditation Institution | 6/6 | Professional Bachelor’s degree |
| Universitet | University | The Danish Accreditation Institution | 6-8/6-8 | Professional Bachelor’s degree, Bachelor’s degree, Master’s degree, PhD degree |
| Kunstnerisk uddannelsesinstitution | Institutions in architecture and art | The Danish Accreditation Institution | 6-8/6-8 | Bachelor’s degree, Master’s degree |
| Maritim uddannelsesinstitution | Maritime educational institutions | The Danish Accreditation Institution | -6/-6 | Professional Bachelor’s degree |
3. Types of higher education
| Qualification | Qualification in English | EQF level / Cycle | Length or ECTS | Access requirement | Access to further study |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Erhvervsakademigrad | Academy profession degree | 5 / Short cycle | 90-150 ECTS | Upper secondary or VET | May give access to top-up professional bachelor’s programmes |
| Bachelorgrad | Bachelor’s degree | 6 / First cycle | 180 ECTS | Upper Secondary | Master’s degrees |
| Professionsbachelorgrad | Professional bachelor’s degree | 6 / First cycle | 180-270 ECTS | Upper Secondary | Master’s degrees |
| Kandidatgrad | Master’s degree | 7 / Second cycle | 120-180 ECTS | A bachelor’s degree or a professional bachelor’s degree | Ph.D. Degree |
| Ph.d.-grad | PhD degree | 8 / Third cycle | 180 ECTS | A master’s degree | n/a |
3.1. Adult and continuing higher education
In Denmark there are two different pathways in higher education. One pathway is the ordinary formal higher education system aimed at students coming with general upper secondary qualifications, while the second pathway is aimed at adults with at least two years of relevant work experience (called adult/continuing higher education). The Academy Profession degree within adult/continuing higher education is awarded after studies at short cycle level and gives access to diploma programmes. The Diploma degree (diplomuddannelse) is awarded after studies at first cycle level and gives access to master programmes. The Master degree (masteruddannelse) is awarded after studies at second cycle level, but does not give access to PhD. The ordinary system includes the degrees mentioned in the table above.
The programmes normally consist of 2 years of part-time study (60 ECTS credits). Certain master programmes require 90 ECTS credits. Degrees in the adult/continuing education system are in general professionally oriented and aimed at developing professional practice and management competences within the different subject areas.
4. Qualifications framework
The qualification levels form the basis for the Danish National Qualifications Framework for Higher Education, which is certified in accordance with the overarching Bologna Framework according to the principles adopted by the European Ministers of Higher Education. Danish higher education qualifications at levels 5-8 of the Danish Qualifications framework for Lifelong Learning (NQF) are also compatible with levels 5-8 of the European Qualifications Framework (EQF).
5. Quality assurance and accreditation
Accreditation is mandatory for all institutions of higher education and a precondition for attaining public funding.
With the Accreditation Act of 2013, the system has gradually switched from accreditation of individual programmes to accreditation of entire education institutions. During a transitional period, there continues to be accreditation of existing and new programmes offered by education institutions that have not yet obtained a positive institutional accreditation.
Denmark has implemented the Standards and Guidelines for Quality Assurance in the European Higher Education Area (ESG), and all public higher education study programmes must meet these international quality and relevance standards.
The Danish Qualifications Framework has been incorporated into the quality criteria of the accreditation system.
For more information see:
- Accreditation and quality assurance – Danish Agency for Higher Education and Science
- The Danish Accreditation Institution
6. Upper secondary qualifications giving access to higher education
| Name | Specialisation | Further study |
|---|---|---|
| Higher General Examination (studentereksamen, STX) | General education and general study preparation | All short and first cycle programmes |
| Higher Preparatory Examination (højere forberedelseseksamen, HF) | General study preparation | Professionally-oriented short and first cycle programmes, i.e. Academy Profession and Professional Bachelor’s programmes |
| Higher Preparatory Examination, addition courses included (højere forberedelseseksamen, HF, med overbygning) | General study preparation | All short and first cycle programmes |
| Higher Technical Examination (teknisk studentereksamen, HTX) | Focuses on subjects related to the fields of technical sciences, natural sciences and informatics | All short and first cycle programmes |
| Higher Commercial Examination (merkantil studentereksamen, HHX) | Focuses on subjects related to the fields of business economics, marketing and international economics | All short and first cycle programmes |
| EUX | Combines a vocational education and training programme with general upper secondary education | All short and first cycle programmes |
