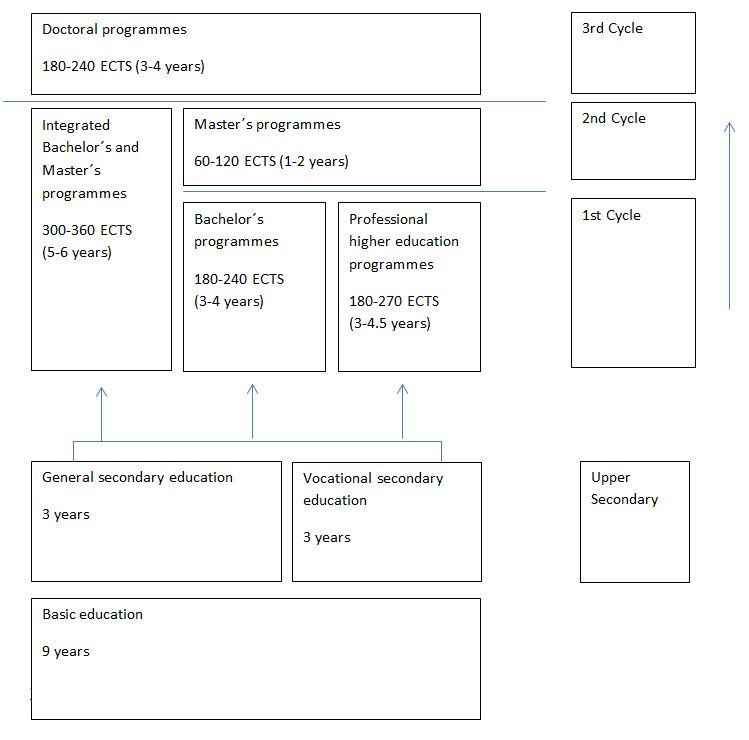
1. Diagram of the Estonian higher education system
2. Types of higher educational institutions
| National name | English name | Quality Assurance | NQF/ EQF | Types of qualifications offered |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rakenduskõrgkool | Professional higher education institution | Estonian Higher Education Accreditation Centre | 6-7 | Professional higher education and master’s degrees |
| Ülikool | University | Estonian Higher Education Accreditation Centre | 6-8 | Professional higher education, bachelor’s, master’s and doctoral degrees |
In addition to universities and professional higher education institutions, vocational education institutions may offer professional higher education programmes. As of 2015 there are two vocational education institutions providing professional higher education programmes:
- Tallinna Majanduskool (Tallinn School of Economics)
- Võrumaa Kutsehariduskeskus (Võru County Vocational Education Training Centre)
3. Types of higher education
| Qualification | Qualification in English | EQF level / cycle | Length or ECTS | Access requirement | Access to further study |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bakalaureus | Bachelor | 6 / 1st cycle | 180-240 ECTS credits | Gümnaasiumi lõputunnistus (Certificate of General Secondary Education) or a corresponding qualification | Master´s programme |
| Rakenduskõrghariduse diplom | Diploma of Professional Higher Education | 6 / 1st cycle | 180-270 ECTS credits | Gümnaasiumi lõputunnistus (Certificate of General Secondary Education) or a corresponding qualification | Master´s programme |
| Magister | Master | 7 / 2nd cycle | 60-120 ECTS credits (together with a first cycle degree no less than 300 ECTS credits) | Bakalaureus (Bachelor) or Rakendus-kõrghariduse diplom | Doctoral programme |
| Arstikraad / Hambaarstikraad / Farmaatsiamagister / Loomaarstikraad / Arhitektuurimagister / Tehnikateaduse magister / aridusteaduse magister | Degree in Medicine / Degree in Dentistry / Master of Science in Pharmacy / Degree in Veterinary Medicine / Master of Science in Architecture / Master of Science in Engineering / Master of Arts in Education | 7 / long cycle | 300-360 ECTS credits | Gümnaasiumi lõputunnistus (Certificate of General Secondary Education) or a corresponding qualification | Doctoral programme |
| Filosoofiadoktor | Doctor of Philosophy | 8 / 3rd cycle | 180-240 ECTS credits | Magister (Master) or a long-cycle degree | n.a. |
Recognition and comparison of Estonian pre-Bologna higher education qualifications issued until 2007 are regulated at national level by Government Regulation No.120; 06.06.2005 (RT I 2005, 32, 241).
4. Qualifications framework
The qualification levels form the basis for the Estonian National Qualifications Framework for Higher Education, which is certified in accordance with the overarching Bologna Framework according to the principles adopted by the European Ministers of Higher Education.
Estonian higher education qualifications at levels 6-8 of the Estonian Qualifications framework for Lifelong Learning (NQF) are also compatible with levels 6-8 of the European Qualifications Framework (EQF). There are no higher education qualifications at level 5 in the Estonian National Qualifications Framework for Higher Education.
See also:
5. Quality assurance and accreditation
Assessment of study programmes began after the foundation of Eesti Kõrghariduse Akrediteerimiskeskus (Estonian Higher Education Accreditation Centre, EHEAC) in 1997. Until 2008 accreditation was the responsibility of the EHEAC and the Kõrghariduse Hindamise Nõukogu (Higher Education Quality Assessment Council, HEQAC). The HEQAC was founded by the Government in 1995 and operated under the administrative jurisdiction of the Ministry of Education and Research.
The system of quality assessment consisted of four parts – self-analysis of higher education institutions (faculties or departments), a foreign expert appraisal, the decision by the HEQAC, and self-improvement of the higher education institution.
Since 2009 higher education quality has been assessed by an independent agency Eesti Kõrghariduse Kvaliteediagentuur (Estonian Higher Education Quality Agency, EKKA). The responsibility of the agency is to conduct institutional accreditation of higher education institutions and quality assessment of study programme groups.
Higher education institutions are required to undergo institutional accreditation once every seven years, but if EKKA has detected any defects in the previous accreditation, it may grant a term of up to three years. The institutional accreditation is an external evaluation within it is assessed the management, administration, academic and research activity, and academic and research environment of higher education institution.
Quality assessment of study programme groups takes also place once in seven years, unless EKKA has set an earlier deadline based on the results of the previous evaluation. Within the assessment process of study programme groups it is assessed if the programmes correspond with the current legislation and with the national and international standards, including the quality of theoretical and practical training, the qualifications of the teaching and research staff, as well as the availability of the necessary resources. On the basis of external assessment, the higher education institution has the right to conduct studies according to the programme belonging to the respective study programme group.
The decision on institutional accreditation and quality assessment of study programme groups will be made by the EKKA Quality Assessment Council.
6. Upper secondary qualifications giving access to higher education
| Name | Specialisation | Further study |
|---|---|---|
| Gümnaasiumi lõputunnistus (Certificate of General Secondary Education) | General secondary education preparation | All first cycle programmes |
| Keskkooli lõputunnistus (Certificate of General Secondary Education, issued until 1995) | General secondary education preparation | All first cycle programmes |
| Kutsekeskhariduse lõputunnistus (Certificate of Vocational and Secondary Education) | Vocational and General secondary education preparation | All first cycle programmes |
| Lõputunnistus kutsekeskhariduse omandamise kohta (Certificate of Vocational Secondary Education, since admission 2006) | Vocational and General secondary education preparation | All first cycle programmes |
| Lõputunnistus põhihariduse basil kutsekeskhariduse omandamise kohta (Certificate of Vocational Secondary Education Based on Basic Education, until admission 2005) | Vocational and General secondary education preparation | All first cycle programmes |
| Lõputunnistus keskerihariduse omandamise kohta (Certificate of Specialised Secondary Education, until admission 1999) | Vocational and General secondary education preparation | All first cycle programmes |
| Lõputunnistus kutse- ja keskhariduse omandamise kohta (Certificate of Vocational and Secondary Education, until admission 1998) | Vocational and General secondary education preparation | All first cycle programmes |
| Diplom [keskerihariduse omandamise kohta] (Diploma [of Specialised Secondary Education], until admission 1994) | Vocational and General secondary education preparation | All first cycle programmes |
