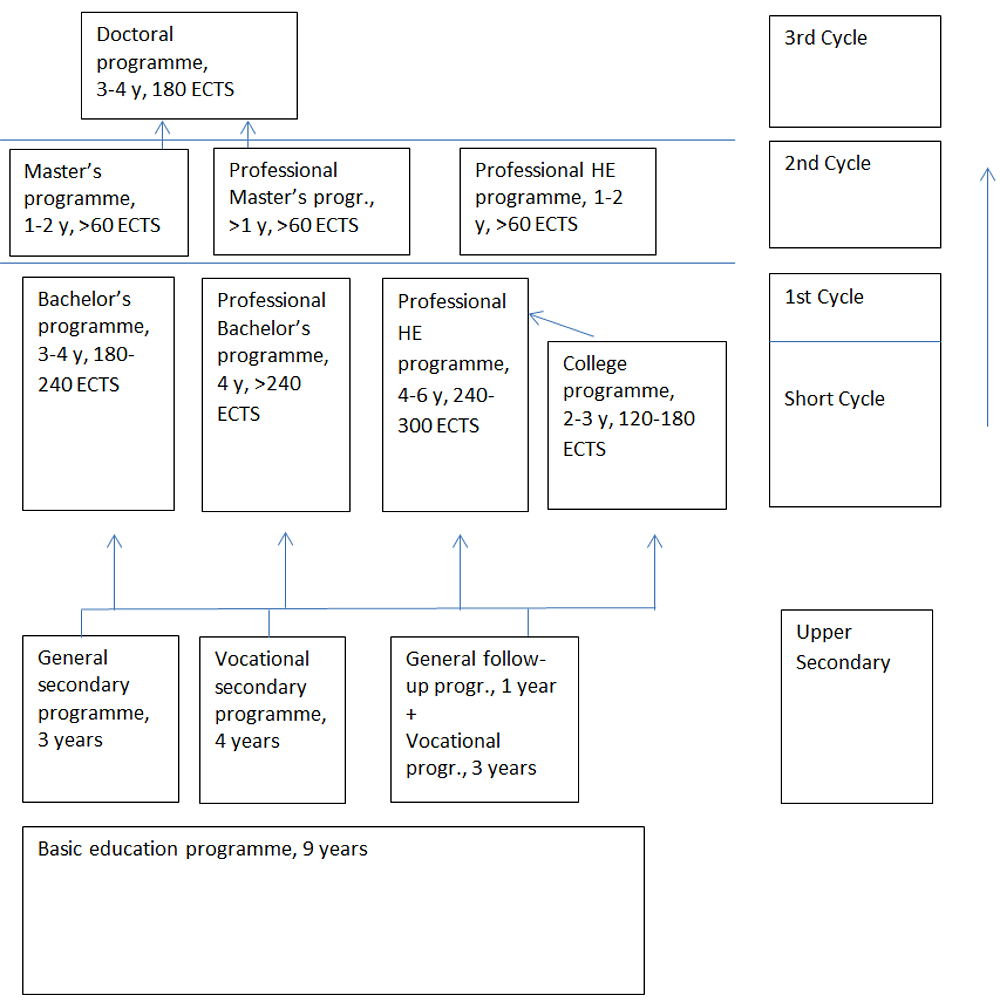
1. Diagram of the Latvian higher education system
2. Types of higher educational institutions
| National name | English name | Accreditation of institution | EQF/NQF | Types of qualifications offered |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Augstskola | Institution of higher education | Higher Education Council | 5-8 | All types of higher education qualifications |
| Akadēmija | Academy | Higher Education Council | 5-8 | All types of higher education qualifications |
| Universitāte | University | Higher Education Council | 5-8 | All types of higher education qualifications |
| Koledža | College | Higher Education Council | 5 | First level professional higher education diploma |
Titles of HEIs are stipulated by the Law on Institutions of Higher Education (last amended on 12 September 2013):
Information about accredited study fields is under preparation.
3. Types of higher education
| Qualification | Qualification in English | EQF/ NQF level, cycle | Length/ECTS | Access requirement | Access to further study |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pirmā līmeņa profesionālās augstākās izglītības diploms | First level professional higher education diploma | 5, short cycle | 120-180 ECTS | General or vocational secondary education | Studies at bachelor, professional bachelor or second level professional higher education programmes. NB! When enrolling the same branch bachelor programme, part of credit points can be transferred from previous studies |
| Bakalaura diploms | Bachelor’s diploma | 6, 1st cycle | 180-240 ECTS | General or vocational secondary education | Studies at master, professional master or second level professional higher education programmes |
| Profesionālās augstākās izglītības diploms vai augstākās profesionālās kvalifikācijas diploms | Professional higher education diploma or higher professional qualification diploma | 6, 1st cycle | at least 240 ECTS, total duration of HE studies at least 4 years | First level professional higher education | Master studies |
| Profesionālās augstākās izglītības diploms vai augstākās profesionālās kvalifikācijas diploms | Professional higher education diploma or higher professional qualification diploma | 6, 1st cycle | at least 60 ECTS, total duration of HE studies at least 4 years | Academic or professional Bachelor’s degree, second level professional higher education | Master studies |
| Profesionālā bakalaura diploms un augstākās profesionālās kvalifikācijas diploms | Professional Bachelor’s diploma and higher professional qualification diploma | 6, 1st cycle | at least 240 ECTS | General or vocational secondary education | Master studies |
| Maģistra diploms | Master’s diploma | 7, 2nd cycle | at least 60 ECTS, total duration of HE full time studies at least 5 years | Academic or professional Bachelor’s degree, second level professional higher education | Doctoral studies |
| Profesionālā maģistra diploms un augstākās profesionālās kvalifikācijas diploms | Professional Master’s diploma and higher professional qualification diploma | 7, 2nd cycle | at least 60 ECTS, total duration of HE studies at least 5 years | Academic or professional Bachelor’s degree, second level professional higher education (after at least 4 year full time studies) | Doctoral studies |
| Profesionālās augstākās izglītības diploms vai augstākās profesionālās kvalifikācijas diploms | Professional higher education diploma or higher professional qualification diploma | 7, 2nd cycle | at least 300 ECTS | General or vocational secondary education | Doctoral studies (after medical studies medical residency) |
| Doktora diploms | Doctoral diploma | 8, 3rd cycle | 180 ECTS | Academic or professional Master’s degree | n.a. |
The system of higher education comprises academic higher education (akadēmiskā augstākā izglītība) leading to a degree and professional higher education (profesionālā augstākā izglītība) leading to a degree and professional qualification. The aim of academic higher education is to prepare for independent research activities and to provide theoretical basis for professional activities.
The aim of professional higher education is to ensure the acquisition of in-depth knowledge in a concrete field, ensuring the graduates’ ability to develop or improve systems, products and technologies and to prepare the graduates for creative, research and pedagogical work in this field.
In HE Latvian credit points (CP) are used, which are defined as the amount of one-week workload of full-time studies. The average workload for one year of full-time studies is 40 CP. The Latvian credit point system is compatible with ECTS. Recalculating the Latvian CP into the ECTS credits, the amount of Latvian CP has to be multiplied by 1.5.
4. Qualifications framework
The Latvian Qualifications Framework (LQF) is established and has been presented to the EQF Advisory Group in 2011. It consists of eight levels. Descriptors of the LQF are based on learning outcomes. The framework includes formal (general/academic and vocational/professional) education: basic, secondary and higher.
In 2010, the LQF level descriptors were included in the Cabinet of Ministers “Regulations on the classification of Latvian education” (2008). Similar to the EQF, they are expressed as:
- Knowledge (knowledge and comprehension),
- Skills (ability to apply knowledge, communication, general skills) and
- Competence (analysis, synthesis and assessment).
LQF was legally strengthened by the Amendments to the Education Law in June 2015, which defined LQF and provided general level descriptors.
The Latvian higher education framework, which is a part of the LQF, is based on three Bologna cycles: bachelor, master and doctor. The cycle descriptors are based on learning outcomes.
The Cabinet of Ministers “Regulations on the classification of Latvian education”:
The Latvian referencing report (second version, May 2012) is available here:
5. Quality assurance and accreditation
Accreditation is carried out according to the Law on Higher Education Institutions (1995), article 9, which stipulates the general accreditation principles of higher education institutions (HEI). Only those higher educational establishments which have received license and offer state accredited study programmes have the right to issue HE qualifications recognised in Latvia.
Institutional accreditation
Higher Education Council (Augstākās izglītības padome) is responsible for higher education quality. The Higher Education Council takes decision on the accreditation of higher education institution as a whole and submits it to the MoES for approval.
Programme accreditation
In 2012, a new HE accreditation and quality management model was implemented – from accreditation of separate study programmes to the accreditation study fields (According to the Cabinet of Ministers “Regulations for accreditation of higher education institutions, colleges and study fields”, 2012). The Agency responsible for organization of the accreditation process for study fields is the Academic Information Centre (since July 1, 2015).
6. Upper secondary qualifications giving access to higher education
| Title | Specialisation | Further studies |
|---|---|---|
| Secondary school (vidusskola) | General secondary education | All first cycle programmes |
| Gymnasium (ģimnāzija) | General secondary education | All first cycle programmes |
| Evening school (vakarskola) | General secondary education | All first cycle programmes |
| Vocational secondary school (profesionālā vidusskola) | Vocational secondary education | All first cycle programmes |
| Technical school (tehnikums) | Vocational secondary education | All first cycle programmes |
| Some colleges (koledža) | Vocational secondary education | All first cycle programmes |
All secondary education students (both vocational and general) take final state centralized exams in Latvian, Math, foreign language and one in optional study subject (student’s choice). Students receive a certificate of general secondary education (vispārējās vidējās izglītības sertifikāts), which – together with certificate of general secondary education (atestāts par vispārējo vidējo izglītību) or diploma of vocational secondary education (diploms par profesionālo vidējo izglītību) – gives the right to enrol higher education programmes.
