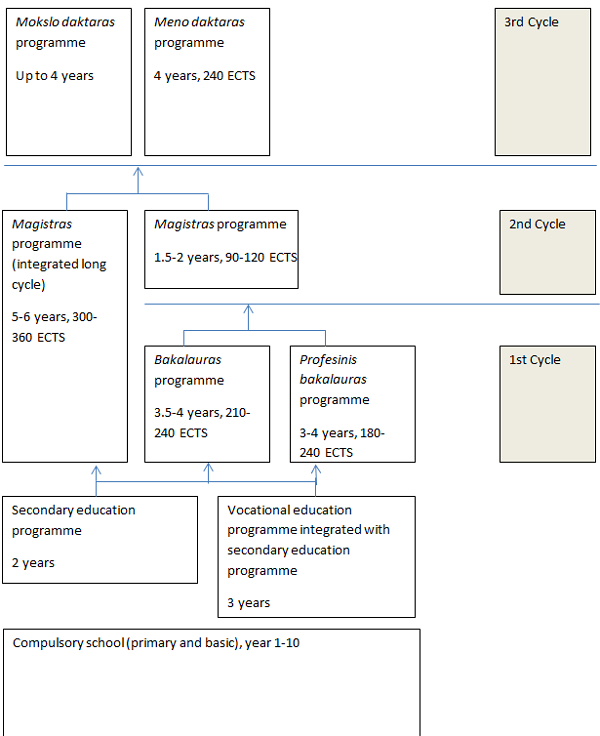
1. Diagram of the Lithuanian higher education system
2. Types of higher educational institutions
| National name | English name | Accreditation | NQF level | Types of qualifications offered |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kolegija | Colleges of higher education | Centre for Quality Assessment in Higher Education (SKVC) | 6 | Professional Bachelor degree |
| Universitetas | Universities | Centre for Quality Assessment in Higher Education (SKVC); Lithuanian Research Council (LMT, only NQF level 8) | 6-8 | Bachelor degree, Master degree, Doctoral degree |
Individual colleges of higher education can alternatively use the title of aukštoji mokykla (higher education institution).
Individual universities can alternatively use the title of akademija (academy) or seminarija (seminary).
3. Types of higher education
| Qualification | Qualification in English | Level EQF/Cycle | Length or ECTS | Access requirement | Access to further study |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bakalauras | Bachelor | 6/1 cycle | 210-240 ECTS | Brandos atestatas (Maturity Certificate) | Master programmes |
| Profesinis bakalauras | Professional Bachelor | 6/1 cycle | 180-240 ECTS | Brandos atestatas (Maturity Certificate) | Master programmes |
| Magistras | Master | 7/2 cycle | 90-120 ECTS | Bakalauras (Bachelor) Or Profesinis bakalauras (Professional Bachelor) | Doctoral programmes |
| Magistras (long cycle) | Master | 7/ 2 cycle | 300-360 ECTS | Brandos atestatas (Maturity Certificate) | Doctoral programmes |
| Mokslo daktaras | Doctor of Science | 8/3 cycle | up to 4 years | Magistras (Master) | n/a |
| Meno daktaras | Doctor of Arts | 8/3 cycle | 240 ECTS | Magistras (Master) | n/a |
Non-degree granting higher education programmes
In addition to the regular degree granting studies, the Lithuanian system of higher education also has non-degree granting studies. The programmes can be provided by colleges and universities and do not lead to a degree. The aim of the programmes is to prepare for independent professional practice and/or to upgrade or acquire a new professional qualification on the basis of previous education. The programmes are offered for those who already have a higher education qualification.
Currently two types of non-degree granting programmes are offered:
- residency (rezidentūra) programmes in medicine, odontology, and veterinary medicine;
- programmes in pedagogical studies (pedagoginės studijos).
Duration of residency studies is from 2 to 6 years. Rezidentūros pažymėjimas (Certificate of Residency) is awarded after completion of residency studies.
The workload of non-degree pedagogical studies is from 30 to 120 credits. Studijų pažymėjimas (Certificate of Studies) is issued after completion of other non-degree granting studies.
4. Qualifications framework
The Lithuanian Qualifications Framework (LTQF) was approved in 2010 and referenced to the European Qualifications Framework for Life Long Learning (EQF) in 2012.
LTQF is a comprehensive framework as it encompasses all sectors of formal education. The framework consists of 8 levels, which directly correspond to the 8 EQF levels.
5. Quality assurance and accreditation
External quality evaluation and/or accreditation in Lithuania is carried out by the Centre for Quality Assessment in Higher Education (SKVC) which was established in 1995. The following types of accreditation and licensing are currently applicable in the Lithuanian system of higher education:
- programme accreditation (ex-ante and ex-post);
- institutional accreditation;
- licensing to establish a new higher education institution.
Quality assurance in doctoral studies and research is carried out by the Lithuanian Research Council (LMT).
Programme accreditation
External evaluation of study programmes for accreditation purposes started in 1998. Programme accreditation is applicable to the first and second cycle programmes. In Lithuania, a study programme has to be accredited before it can be offered by a higher education institution. The evaluation can be carried out by SKVC or any other agency listed in the EQAR. In all cases, either upon evaluation reports by an agency in EQAR, or based on evaluation reports by expert panels organized by SKVC, the final accreditation decision is made by SKVC. Other accreditation requirements apply for programmes in the field of theology and priest seminaries.
All new study programmes are checked for compliance with national legislation and can be accredited for a period of one year longer than the full duration of the study programme (ex-ante accreditation). Running programmes can be accredited for 3 years, 6 years, or not accredited (ex-post accreditation). In case of non-accreditation, student enrolment is discontinued; current students can be transferred into another programme or an institution can be allowed to finish implementation of the programme within a specified period upon urgent implementation of quality amelioration plans.
Institutional accreditation
Institutional review and accreditation was launched in 2011. It is aimed at enhancing the culture of quality and improvement of the provision of higher education, as well as establishing compliance with the requirements of Lithuanian legislation and the principles of the European Higher Education Area. Higher education institutions can be accredited for 6 or 3 years depending on the results of the institutional review. In case of a negative review outcome, a repeated evaluation within a period of two years is carried out.
6. Upper secondary qualifications giving access to higher education
| Name: | Specialisation | Further study |
|---|---|---|
| Brandos atestatas (Maturity Certificate) | General education and general study preparation. The programme can also be offered as an integrated programme together with vocational education and training programmes. | All first and long cycle programmes |
Graduation requirements include passing final examinations, which can be offered and organized on state level and/or school level.
