1. Diagram of the Norwegian higher education system
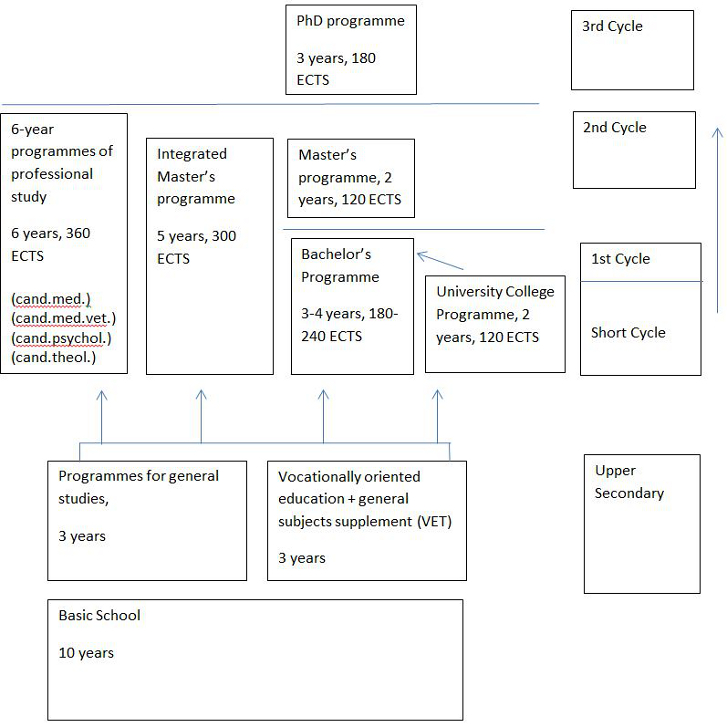
2. Types of higher educational institutions
| National name | English name | Accreditation | EQF levels | Types of qualifications offered |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Universitet | University | NOKUT | 6 – 8 | University college degree, bachelor’s degree, master’s degree, ph.d., dr.philos. |
| Vitenskapelig høyskole | Specialized University College | NOKUT | 6 – 8 | University college degree, bachelor’s degree, master’s degree, ph.d., dr.philos. |
| Høyskole | University of Applied Science, University College | NOKUT | 6 – 8 | University college degree, bachelor’s degree, master’s degree, ph.d. |
| Høyskole med akkrediterte studietilbud | University College with accredited study programmes | NOKUT | 6 – 7 | Bachelor’s degree, master’s degree |
List of publicly recognised higher education institutions:
List of accredited study programs at university colleges without institutional accreditation:
3. Types of higher education
| Qualification | Qualification in English | EQF level / Cycle | Length or ECTS | Access requirement | Access to further study |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Høyskolekandidat-grad | University college degree | 6 / Short cycle | 120 ECTS | The Higher Education Entrance Qualification or corresponding qualification | Access / transfer to bachelor’s degree |
| Bachelorgrad | Bachelor’s degree | 6 / 1st Cycle | 180-240 ECTS | The Higher Education Entrance Qualification or corresponding qualification | Master’s degree |
| Mastergrad | Master’s degree Master’s degree – long-cycle | 7 / 2nd Cycle | 120 / 300 ECTS * | A bachelor’s degree or equivalent qualification. Additional requirements may apply. | PhD degree |
| Doktorgrad (ph.d.) | Ph.D. degree | 8 / 3rd Cycle | 180 ECTS | A master’s degree or equivalent qualification. Additional requirements may apply. | n/a |
* In the subject areas of medicine, veterinary medicine, psychology and theology, six-year one-tier programmes of professional study (360 ECTS) lead up to special second cycle degrees. The programmes confer the following titles: Candidata/candidatus medicinae (cand.med.), Candidata/candidatus medicinae veterinariae (cand.med.vet.), Candidata/candidatus psychologiae (cand.psychol.), Candidata/candidatus theologiae (cand.theol.). See: Master’s degree – long cycle
One-year programmes/supplementary programmes/short programmes
Universities and university colleges offer many one-year programmes, supplementary programmes and short programmes (årsstudier/påbygningsstudier/kortere studier). Many of them can form part of bachelor’s degrees, and some can also form the basis for programmes of professional study in the subject, for example in psychology.
Lifelong learning
Adult education in Norway aims to enable adults to acquire necessary basic skills and allow them to formalise and develop their qualifications. The municipalities and county authorities are responsible for providing primary and secondary education for adults.
Continuing and further education programmes allow people to update their competence and improve their ability to adapt. Such programmes are intended to ensure that enterprises and organisations have employees with the necessary knowledge and skills.
- Further education programmes lead to new formal
qualifications at university and university college level (programmes
for which ECTS credits are awarded). Some master’s degree programmes
are based on relevant work experience in addition to academic
specialisation in the bachelor’s degree. Such programmes are called
experience-based programmes, and their scope can be either two years
(120 ECTS credits) or one and a half years (90 ECTS credits). The
admission requirements are a relevant educational qualification and
minimum 2 years of relevant work experience. The experience-based
master’s degree programmes do not qualify alone for admission to
PhD.
- Continuing education consists of shorter courses
updating existing qualifications, and no ECTS credits are
awarded.
4. Qualifications framework
The Norwegian Qualifications Framework for lifelong learning (NQF) from 2011 provides a description of the formal Norwegian education and training system. The Norwegian qualifications framework (NQF) consists of seven levels (there are no qualifications at level 1).
NQF was referenced to the European Qualifications Framework (EQF) in 2014. A report referencing the levels of the NQF to the levels of the European Qualifications Framework of Lifelong learning (EQF) was presented by the Ministry of Education and Research in June 2014. In addition, the report presents the self-certification (assessment of compatibility) of the qualifications framework against the Bologna framework (QF-EHEA).
Levels 2-8 in the NQF are referenced to levels 2-8 in the EQF, while levels 6-8 of the NQF also correspond with the first, second and third cycle of the QF-EHEA.
NQF levels are formulated in terms of learning outcomes, which are expressed in the categories of knowledge, skills and competence that graduates at various levels should have achieved. The NQF also gives an overview of degrees, diplomas, certificates, craft or journeyman’s certificates and documents of skill.
With time, qualification certificates, diplomas and other relevant documents will contain a clear reference to the appropriate EQF level, and the NQF will be adopted into Norwegian law as a regulation.
5. Quality assurance and accreditation
NOKUT (Norwegian Agency for Quality Assurance in Education) is the controlling authority for educational activity at all Norwegian universities, special field universities, university colleges and institutions with single accredited higher education programmes.
Through an evaluation procedure NOKUT decides on the recognition of the institutions’ internal quality assurance systems and carries out checks to see if their educational provision meets national quality standards.
6. Upper secondary qualifications giving access to higher education
The Norwegian Universities and Colleges Admission Service (NUCAS, in Norwegian: Samordna opptak), coordinates the admission to ordinary undergraduate study programmes at all universities, university colleges, and some private university colleges in Norway.
There are several ways of fulfilling the requirements of the Higher Education Entrance Qualification:
| Name | Details / Specialisation | Access to further study |
|---|---|---|
| Completed upper secondary education | The Certificate of Upper Secondary Education and Training (Vitnemål for videregående opplæring) is based on 13 years of schooling. Fulfils all higher education entrance requirements. | All first cycle programmes |
| Completed upper secondary education | Fulfils higher education entrance requirements together with supplementary studies qualifying for higher education (6 additional subjects). | All first cycle programmes |
| ”23/5” path | Fulfils higher education entrance requirements as long as the following criteria are met: Must be 23 or older during the year of application; Must have at least 5 years of work experience or education; Must document completion of supplementary studies qualifying for higher education (6 additional subjects: Norwegian, English, History, Social Science, Mathematics and Natural Science). | All first cycle programmes |
| Steiner Waldorf School | Students who receive a certificate with grades fulfil all higher education entrance requirements. Students who receive a certificate without grades receive an individual evaluation upon application to higher education. | All first cycle programmes |
| Completed two-year programme in tertiary vocational training | Fulfils higher education entrance requirements as long as the programme is approved by NOKUT. Norwegian language requirements apply. | All first cycle programmes |
| Completed one year programme (60 credits) of higher education | Applicants who have been admitted to higher education on the basis of assessment of prior learning and work experience (realkompetanse-vurdering) or similar exemptions, and have completed a one year programme, may fulfil higher education entrance requirements after an individual evaluation. | All first cycle programmes |
| Foreign secondary education | Must fulfil requirements as outlined for each country according to the Higher Education Entrance Qualifications for foreign applicants, GSU List. Academic and Norwegian language requirements apply. | All first cycle programmes |
7. Useful links
- The Norwegian Ministry of Education and Research
- NOKUT (Norwegian Agency for Quality Assurance in Education)
- The Norwegian Qualifications Framework for lifelong learning (NQF) – NOKUT
- Recognized higher education institutions – NOKUT
- Accredited study programs at university colleges – NOKUT
- The Higher Education Entrance Qualifications for foreign applicants (GSU list)
- The Norwegian Universities and Colleges Admission Service (NUCAS)
