1. Diagram of the Swedish higher education system
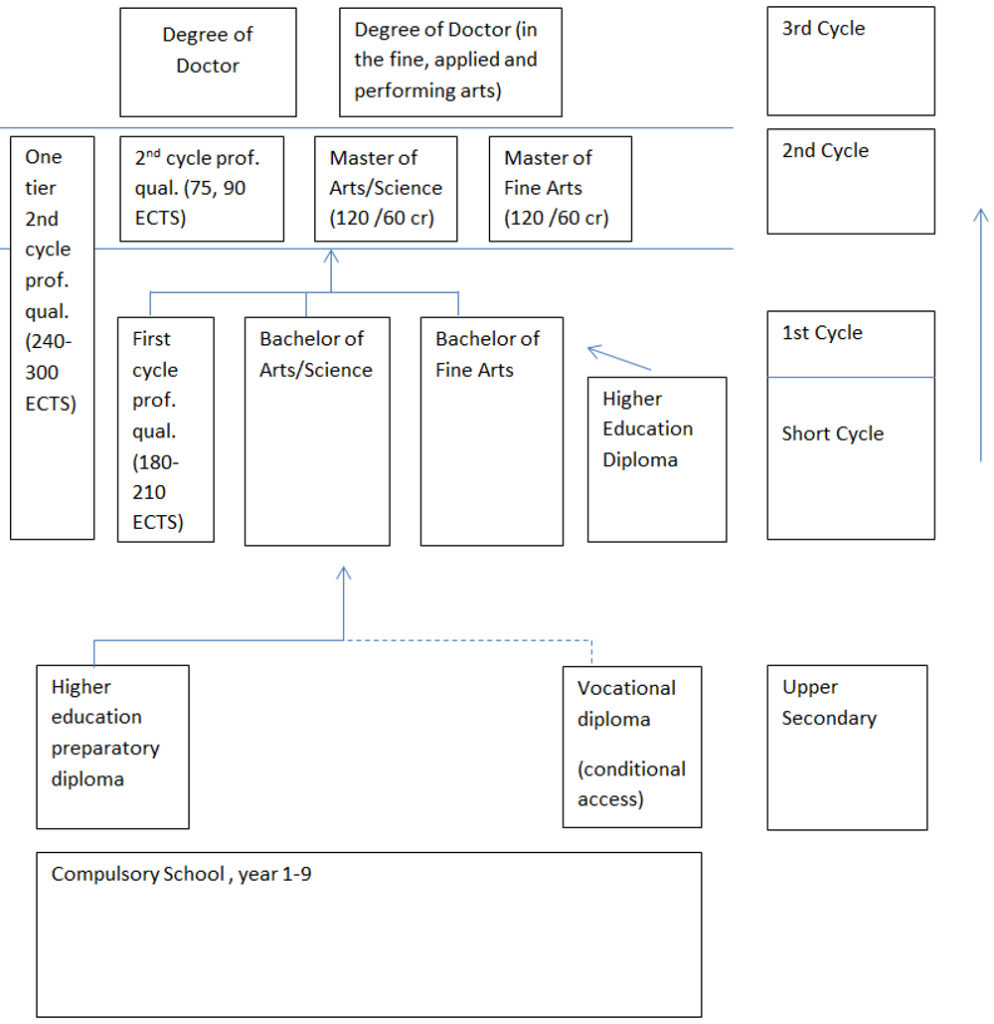
2. Types of higher educational institutions
| Type of institution in original language | English name | Accreditation | NQF level | Types of qualifications offered |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Universitet | University | The Swedish Higher Education Authority | 6-8 | University Diploma, Bachelor’s degree), Professional Bachelor’s degree, Master degrees (one year) Master degrees (two years) Professional Master degrees, Licentiate Degree, Doctoral Degree |
| Högskola | University colleges | The Swedish Higher Education Authority | 6-7 (8) | University Diploma, Professional Bachelor’s degree, Master degree (one year), Other degrees after successful application to the Swedish Higher Education Authority |
| Enskilda utbildnings-anordnare | Independent colleges/university colleges/universities | The Swedish Higher Education Authority | 6-7 (8) | University Diploma, Other degrees after successful application to the Swedish Higher Education Authority, |
3. Types of higher education
| Qualification | Qualification in English | NQF level | Duration, högskolepoäng (ECTS) | Access requirement | Access to further study |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Högskoleexamen | Higher Education Diploma | 6 | 120 hp | Upper Secondary | May give access to top-up bachelor’s programmes |
| Konstnärlig högskoleexamen | Higher Education Diploma in Fine Arts | 6 | 120 hp | Upper Secondary | |
| Kandidatexamen | Degree of Bachelor | 6 | 180 hp | Upper Secondary | Master’s degrees, Diploma and Master programmes |
| Konstnärlig kandidatexamen | Degree of Bachelor in Fine Arts | 6 | 180 hp | Upper Secondary | Master’s degrees (in Fine arts or general) |
| Yrkesexamen på grundnivå (t. ex. högskoleingenjörs-examen, socionomexamen, sjuksköterskeexamen) | Professional qualifications in the first cycle (ex. B.Sc in Engineering, B.Sc. in Social Work, B.Sc. in Nursing) | 6 | 180-210 hp | Upper Secondary | Master’s degrees, Diploma and Master programmes |
| Magisterexamen | Degree of Master (60 credits) | 7 | 60 hp | First cycle degree | Ph.D. |
| Masterexamen | Degree of Master (120 credits) | 7 | 120 hp | First cycle degree | Ph.D. |
| Konstnärlig magister / masterexamen | Degree of Master (60 credits) or (120 credits) in Fine Arts | 7 | 60-120 hp | First cycle degree | PhD or PhD in Fine Arts |
| Yrkesexamen på avancerad nivå (t.ex speciallärarexamen apotekarexamen, arkitektexamen, juristexamen) | Professional qualifications in the second cycle (ex. PGD in Special Needs Training, M.Sc in Pharmacy, M.Architecture, Master of Laws) | 7 | 75-300 hp | A first cycle degree, or, if the programme is a one tier, integrated programme: Upper secondary | Ph.D and Master programmes |
| Licentiatexamen | Licentiate degree | 8 | 120 hp | A second cycle higher education qualification | Continuation to PhD |
| Konstnärlig licentiatexamen | Degree of Licentiate (fine arts) | 8 | 120 hp | A second cycle higher education qualification | Continuation to PhD |
| Doktorsexamen | Degree of Doctor | 8 | 240 hp (or 120 after Licentiate) | A second cycle higher education | n/a |
| Konstnärlig doktorsexamen | Degree of Doctor (fine arts) | 8 | 240 hp | A second cycle higher education | n/a |
The Swedish credit system högskolepoäng (hp) is based on the ECTS, whereas one week of full-time studies represent 1.5 hp, and one year of studies represent 60 hp.
All degrees are awarded within the first, second or third cycle of the Bologna Higher Education Qualifications Framework.
The title of a general qualification (kandidatexamen, magisterexamen, masterexamen) consists of a qualification preceded or followed by a designation indicating the area of specialisation. Each higher education institution determines which designations shall be used. Examples are ekonomie, filosofie, politices, teologie, teknologie kandidatexamen i [specialisation].
Professional qualifications are awarded in the fields of engineering, health care, agriculture, law, education, etc. Professional qualifications may be offered within either the first or the second cycle. Programmes leading to professional qualifications may vary in length depending on their content and may stretch over two cycles. Some professional degrees (approximately 15) are awarded only after one-tier integrated programs.
For access to programmes in Fine Arts, an additional requirement is proof of artistic skills.
4. Qualifications framework
The qualification levels form the basis for the Swedish National Qualifications Framework for Higher Education, which is certified in accordance with the overarching Bologna Framework according to the principles adopted by the European Ministers of Higher Education.
The Swedish parliament decided to implement the Swedish Qualifications framework for Lifelong Learning (NQF) – SeQF with eight levels in July 2015. The SeQF will cover all qualifications throughout the public education system as well as non-formal qualifications. The Swedish National Agency for Higher Vocational Education (MYH) is the responsible Agency.
The referencing report has been sent to the Advisory Group. Consequently, there is no reference to the EQF, only to the NQF in this description of the Swedish Higher Education System.
5. Quality assurance and accreditation
Quality assurance is the shared responsibility of higher education institutions and the Swedish Higher Education Authority (UKÄ). UKÄ replaced the former Swedish National Agency for Higher Education, which was responsible for evaluations up until the end of 2012.
Programmes have to be evaluated on the basis of how well they fulfil the requirements laid down in the Higher Education Act and the Higher Education Ordinance. A new system for quality assurance was introduced at the end of 2016 to replace the old system from 2011. The new quality assurance system follows the European Standards and Guidelines for Quality Assurance in the European Higher Education Area (ESG) and has 4 components:
- Institutional reviews of the Higher Education Institutions’ quality assurance processes
- Programme evaluations
- Appraisal of applications for degree-awarding powers
- Thematic evaluations
As far as degree-awarding powers are concerned, the following applies:
Universities have the right to award first, second and third cycle general qualifications. State university colleges have the right to award first cycle qualifications and magisterexamen (Degree of Master, 60 credits) but must apply to the Swedish Higher Education Authority for the right to award masterexamen (Degree of Master, 120 credits) and third cycle qualifications. State universities and university colleges have to apply to the Swedish Higher Education Authority for the right to award professional qualifications and qualifications in the fine, applied and performing arts.
Independent higher education providers have to apply to the Government for the right to award degrees.
6. Upper secondary qualifications giving access to higher education
The current structure of upper secondary school was introduced 1 July 2011. For students enrolled in upper secondary education before July 2011, the former structure applied through 2011/2012 and 2012/2013.
| Name: | Specialisation | Further study |
|---|---|---|
| Gymnasieskola – Higher education preparatory programme (Högskole-förberedande examen / Higher education preparatory diploma) 2500 credits | 6 national programmes – General education and general study preparation | All first cycle programmes |
| Gymnasieskola – Vocational programme (Yrkesexamen / Vocational diploma) 2500 credits | 12 national programmes – vocational education and preparation for further vocational education | Conditional. A vocational diploma gives access to higher education (first cycle programmes) only if supplemented with passing grades in the following courses: Swedish, or Swedish as a second language 2 and 3, and English 6. If the diploma fulfills the requirements for access to first cycle programmes this is indicated on the diploma. |
| Gymnasieskola – Slutbetyg/Final school grades (Former structure) | National programmes/local variations/specially designed programmes (Former structure) | Conditional – all first cycle programmes. General requirements for access to higher education for holders of Slutbetyg issued 2010 onwards: Students must obtain a total of 2 500 credits, of which passing grades provide 2250 credits (90%). The following courses are always required (with passing grade): Swedish or Swedish as a second language A and B, English A and Mathematics A. Slutbetyg issued 2010 onwards from a Reduced programme does not give access to higher education. |
| Kommunal vuxenutbildning på gymnasial nivå – Municipal adult education – (Högskoleförberedande examen/Higher education preparatory diploma) 2400 credits | General education and general study preparation | All first cycle programmes |
| Kommunal vuxenutbildning på gymnasial nivå – Municipal adult education (Yrkesexamen / Vocational diploma) 2400 credits | Vocational education and preparation for further vocational education | Conditional. A vocational diploma gives access to higher education (first cycle programmes) only if supplemented with passing grades in the following courses: Swedish, or Swedish as a second language 2 and 3, and English 6. If the diploma fulfills the requirements for access to first cycle programmes this is indicated on the diploma. |
| Kommunal vuxenutbildning på gymnasial nivå – Municipal adult education – Slutbetyg/Final school grades 2350 credits (Former structure). Last date of issue: 1 July 2025. | General and/or vocational education and general study preparation (Former structure) | Conditional – all first cycle programmes. General requirements for access to higher education for holders of Slutbetyg issued 2010 onwards: Students must obtain a total of 2350 credits, of which passing grades provide 2250 credits. The following courses are always required (with passing grade): Swedish or Swedish as a second language A and B, English A and Mathematics A. |
7. Useful links
- List of recognized Swedish HE institutions
- Laws and regulations: the Swedish HE Act and Ordinance
- Description of the higher educational system
- The Swedish National Qualifications Framework for higher education (QF-EHEA)
- The certification of the QF-EHEA
- The Swedish Qualifications Framework SeQF (QF-LLL) (so far in Swedish only)
- Swedish ENIC-NARIC
- Information on admissions, study programmes and general info on higher education
- Swedish Higher Education Authority (National quality assurance agency)
- Details of the quality assurance system
- Example of Diploma Supplements: Linköping University
